Conditions
Medical Conditions We Treat ..
Joints & Bones
Frozen Shoulder (Adhesive Capsulitis)
Neck & Spine
Degenerative Disc Disease(DDD)
Herniated Discs(Bulging Discs)/Slipped Disc
Muscles
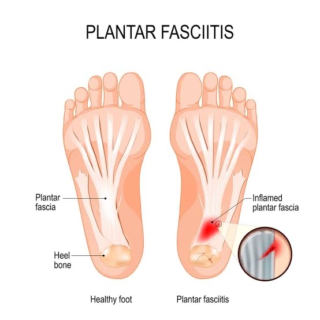
Plantar Fasciitis
Plantar fasciitis is one of the most common conditions causing heel pain. It involves inflammation of the plantar fascia — a tough, fibrous band of tissue that runs along the sole of the foot. The plantar fascia attaches to the heel bone (calcaneus) and to the base of the toes. It helps in supporting & maintaining the arch of the foot and has an important role in normal foot mechanics during walking.
Tension or stress in the plantar fascia increases when you place weight on the foot, such as while standing. The tension also increases when you push off on the ball of the foot and toes. Both of these motions occur during normal walking or running. With overuse or in time, the fascia loses some of its elasticity or resilience and can become irritated with routine daily activities.
Causes
Inflammation and pain in the fascia can be caused by:
- An increase in activity level (like starting a walking or running program)
- The structure or shape of the foot
- The surface on which you are standing, walking or running
- The type of shoes you are wearing
- The weight you carry
Less commonly, plantar fasciitis may develop due to other medical conditions, such as lupus or rheumatoid arthritis.
Symptoms
Plantar fasciitis causes pain in your heel. It’s usually worse when you take your first steps in the morning or after you’ve been sitting for a long time. It tends to feel better with activity but worsens again after you spend a long time in standing.
Risk Factors
You’re at greater risk of plantar fasciitis if you:
- Are female
- Are 40 to 60 years old
- Are obese
- Have flat feet or high arches
- Have tight Achilles tendons, or “heel cords”
- Have an unusual walk or foot position
- Often wear high-heeled shoes
- Spend many hours standing each day
- Wear worn-out shoes with thin soles
Diagnosis
Your doctor will ask about your symptoms and check your feet to see where you’re having pain. They sometimes want you to have imaging tests to make sure something else isn’t causing your problem. These tests include:
- An X-ray to rule out bone fractures or arthritis
- An MRI to look for fractur
